In any electrical system, designing and analyzing the protection scheme is a critical factor in safeguarding personnel, equipment, and maintaining uninterrupted operation. Protection and Relay Coordination study ensure the system responds accurately during faults, swiftly isolates affected areas, and minimizes the impact on the rest of the network.
Why Is Protection & Relay Coordination Study Important?
|
Real-life situation |
Risks Without Protection & Coordination Study |
|
Ground Faults or Short Circuits |
Entire system shutdown instead of localized isolation |
|
Incorrect operation of protective devices |
Production disruption and significant financial loss |
|
Mismatch between new and old equipment |
Devices fail to operate correctly, endangering staff |
|
Lack of regular inspections |
Protection system becomes inaccurate and unreliable over time |
Benefits of Protection and Relay Coordination
- Fast Fault Isolation to minimize outage scope
Ensure that the device closest to the fault responds first, swiftly isolating the affected zone and allowing the rest of the system to continue functioning. - Optimized Relay and protective device settings
Calculate appropriate settings for each system location to prevent false tripping or missed responses between protective components. - Analysis of Time-Current Characteristic Curves
Analysis of Time-Current Characteristic Curves to detect overlaps, miss coordination or hidden risks—then implement solutions that enhance system performance and reliability. - Simulation Sequence of Operation
Test system responses under simulated conditions like short circuits, overloads, and ground faults to assess coordination effectiveness.
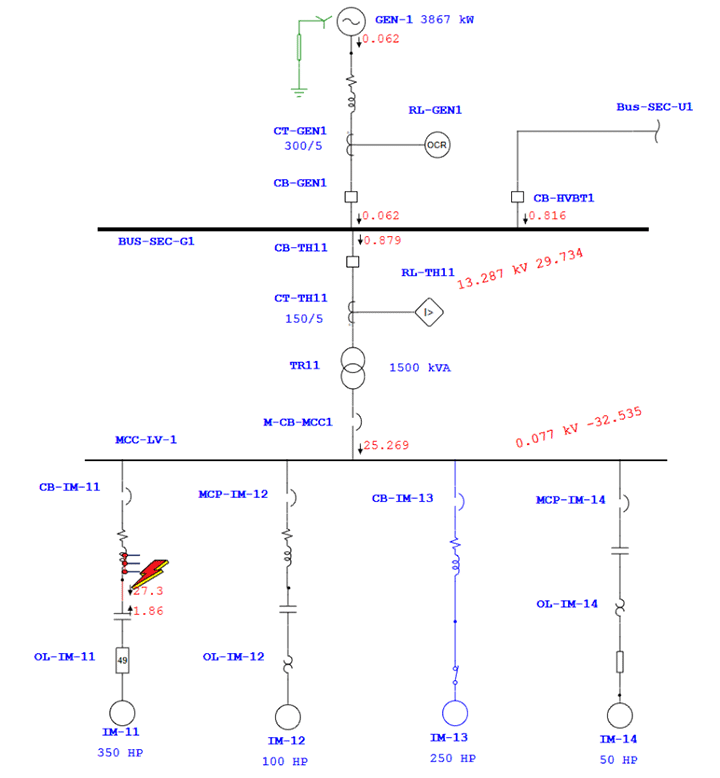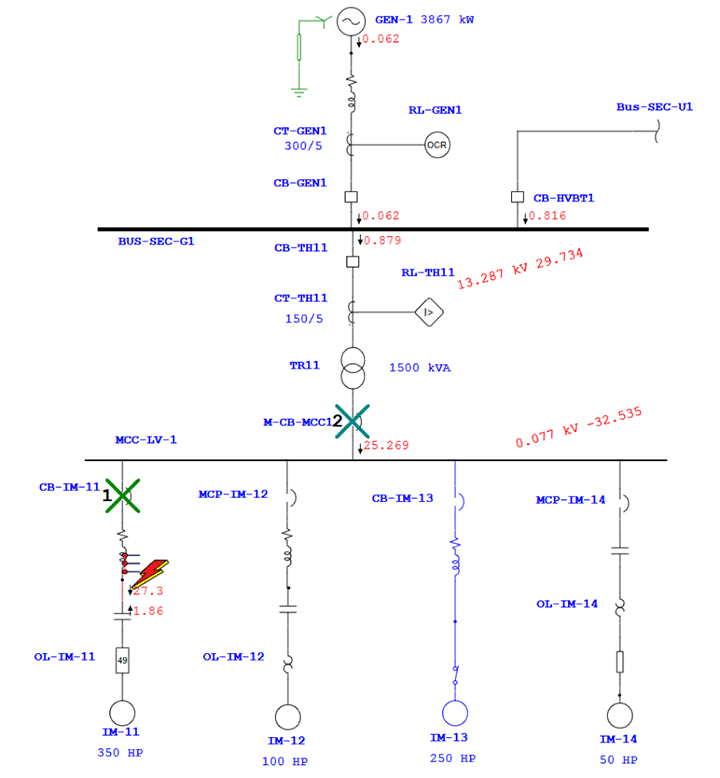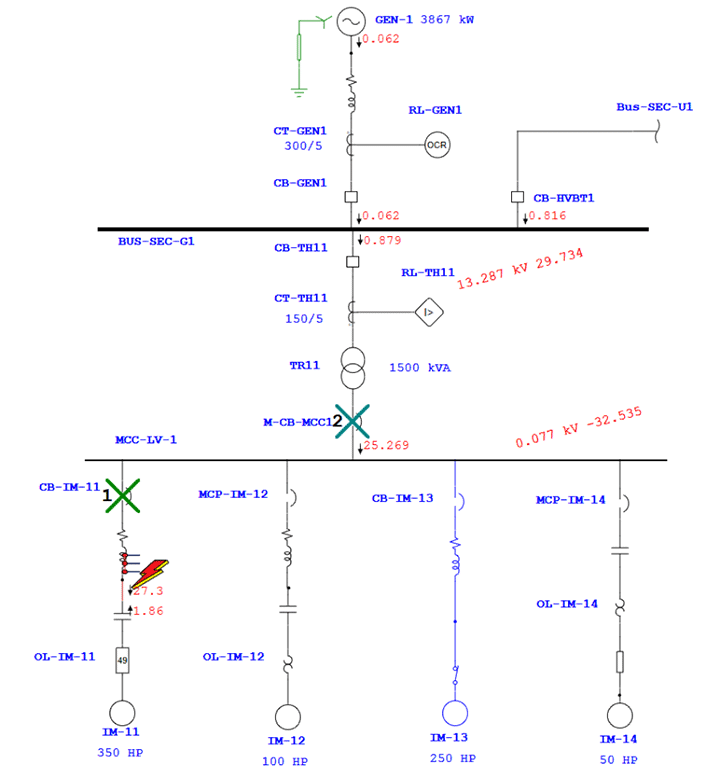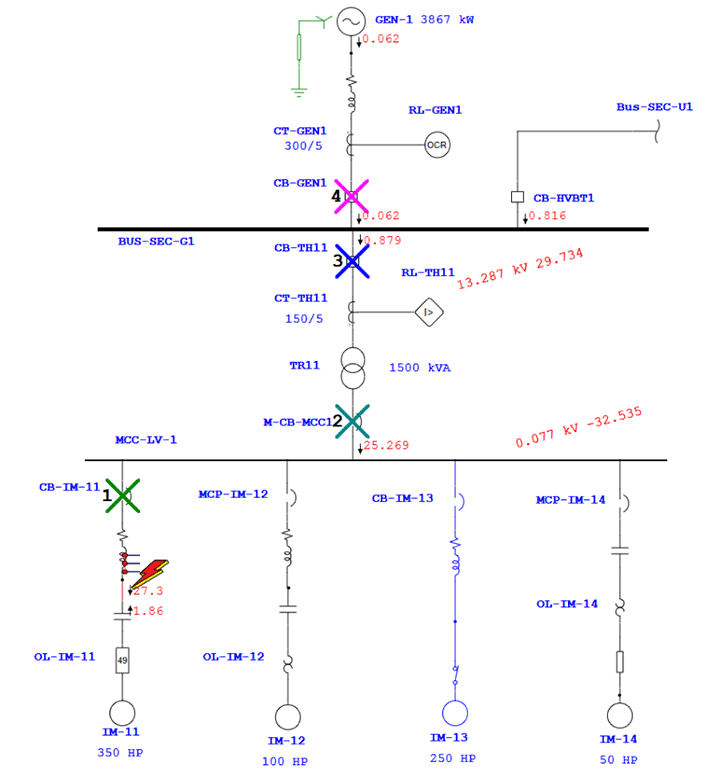
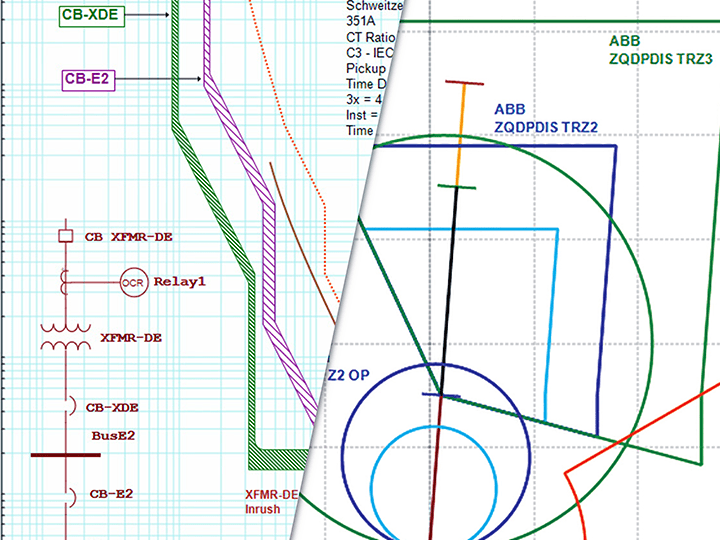
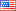
Outcomes Of Protection and Relay Coordination Study
- Detailed report explaining the input data, system configuration, observations and recommendations
- Fault currents at various buses and branches in the system.
- Relay setting tables with recommended and optimized settings
- Time coordination curves
- Sequence of operation
- Input to Arc Flash Study

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt


